Armored fiber cable with build-in metal armor can provide stronger protection of the optical fibers than standards fiber optic cables. It can protect the optical fibers from rodent, oil, impact, etc. What’s more, some armored fiber can provide maximum bend radius. However, various types of armored fiber cables usually make customers confused. There are too many specific details to consider during selection, like fiber counts, jacket type, structure of the armored fiber cable, etc. The superior features make armored fiber cable a perfect fit for campus & building backbones, data centers and industrial applications.This post is something about Armored Fiber Cable you must be know.
Armored Fiber Cable Structure
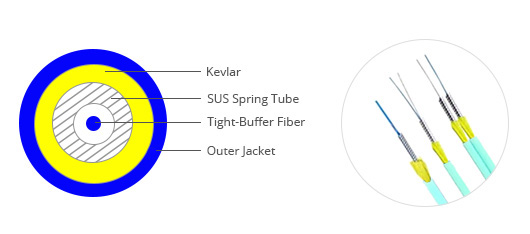
As shown in the below picture, the optical fibers of the armored fiber cable are in the center of the cable covered by metal armor. The metal armor is covered by Kevlar firstly, then by the outer jacket. This is usually the most basic structure of armored fiber cables. For different applications, the structure will change accordingly. Kindly visit “Armored Fiber Cable Structures” for more details about different structure of the armored fiber cable.

Types of Armored Fiber Cable
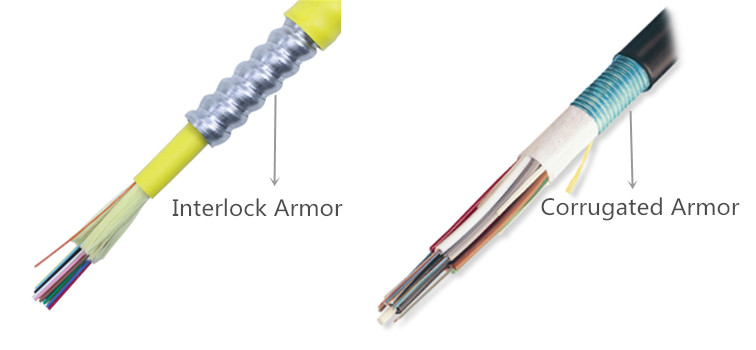
Armored fiber optic cable can be divided into two types according to the metal tube: interlock armored fiber cable and corrugated armored cable. Interlocking armor is an aluminum armor that is helically wrapped around the cable and found in indoor and indoor/outdoor cables. It offers ruggedness and superior crush resistance. Corrugated armor is a coated steel tape folded around the cable longitudinally. It is found in outdoor cables and offers extra mechanical and rodent protection. Both types of these armored fiber cables enable installation in the most hazardous areas, including environments with excessive dust, oil, gas, moisture, or even damage-causing rodents.
Armored Fiber Cable for Indoor and Outdoor Use
Armored fiber cable can be used for indoor, indoor/outdoor and outside plant (OSP) applications. According to different installation environments, tight-buffered armored cable and loose-buffered armored cable are generally adopted: loose-buffer armored fiber cables are usually applied in outdoor applications, while both loose-buffered and tight-buffered armored fiber cable can fit indoor and indoor/outdoor applications.
Indoor Armored Fiber Cable
Armored cable used for indoor applications often consists of tight-buffered or loose-buffered optical fibers, strengths members and an inner jacket. The inner jacket is commonly surrounded by a spirally wrapped interlocking metal tap armor. As the fiber optic communication technology develops rapidly with FTTX, there is a fast growing demand for installing indoor fiber optic cables between and inside buildings. Indoor armored fiber cable experiences less temperature and mechanical stress and it can retard fire effectively.
Indoor/Outdoor Armored Fiber Cable
This armored fiber optic cable shares much popularity in today’s telecommunication network, which allows links from building to building eliminating the transition from indoor cable to outside plant cable. The following picture shows the structure of commonly used multi-fiber I/O armored fiber cable.

Outdoor Armored Fiber Cable
Armored cable for outdoor is made to ensure operation safety in complicated outdoor environment, and most of them are loose buffer design: with the strengthen member in the middle of the whole cable, loose tubes surround the central strength member. Inside the loose tube there is waterproof gel filled to make the cable water resistance. The combination of the outer jacket and the armor protects the fibers from gnawing animals and damages that occur during direct burial installations.
How to Select Armored Fiber Cable?
The selecting of armored fiber cable is like the selection of standard fiber cables. Fiber type (OS2, OM1, OM2, OM3, or OM4), fiber count and cable riser should all be considered. However, there is many special properties of armored fiber cable, the armored fiber cable selection should also consider many other factors.
Armor Type of Armored Fiber Cables
The market can provide armored fiber cables with different types of armor tubes which are with different structures and materials. The most commonly used armor tubes are with interlock design and corrugated design as shown in the above picture. For now, the interlock armored fiber cable is very popular and being used in a lot of indoor and indoor/outdoor applications. Corrugated armored fiber cable is often used in outdoor applications. As for the materiel for armor tube, steel and aluminum are the most commonly used. Now light steel armored fiber cables are being widely used in a lot of indoor applications, because of its lower weight and flexible properties.

Pre-Terminated or Field-Terminated Armored Fiber Cables
As there is a strong metal armored tube inside the armored fiber cable, the termination of armored fiber cable is difficult than that of standard fiber optic cables. In some applications, field-terminated armored fiber cable is better in outdoor applications. While, to save time and ensure transmission quality, many installers will choose pre-terminated armored fiber cables for indoor applications. The pre-terminated armored fiber cables provided by the market are mainly armored fiber patch cable and armored fiber trunk cable. The former looks like the standard fiber patch cable, but it is stronger than the traditional fiber patch cable and is more flexible during cable for it can provide larger bend radius. Pre-terminated armored fiber trunk cable is a length of armored fiber cable with several legs on each ends terminated with fiber optic connectors. Kindly visit “Armored Fiber Cable” page for more specific details about pre-terminated armored fiber cables.
Conclusion
Armored fiber cable presents a premium solution to secure your network by protecting fiber links, which is specified as the primary backbone due to its distinct advantages for space efficiency, lower cost of materials and installation, as well as less risk of downtime and damage.Fiber-Mart offers a great variety of armored cable. and tested rigorously to ensure product reliability and durability, and all the fiber cables are ready in stock for delivery in volume.welcome to contact with us: product@fiber-mart.com.




