Category: Connector & Adapter
All kinds of Fiber Optic Connectors and Adapters, LC, ST, FC, SC, E2000, MPO, MTP, SMA905, MU, DIN etc.
Introduction of Fiber Optic Attenuators
Do you know what is the fiber attenuator used for? As we know, the source of the single mode fiber is laser, the power of which is extremely strong. Therefore we can use single mode fiber to achieve long distance transmission. But, if the transmission distance over single mode fiber is too short, too much light may overload a fiber optic receiver, which may cause serious high bit error rates. How to solve this?
Do you know what is the fiber attenuator used for? As we know, the source of the single mode fiber is laser, the power of which is extremely strong. Therefore we can use single mode fiber to achieve long distance transmission. But, if the transmission distance over single mode fiber is too short, too much light may overload a fiber optic receiver, which may cause serious high bit error rates. How to solve this? Fiber attenuator should be inserted at the receiver end to reduce the power to the proper level. This article sheds light on types, and applications of optical attenuators, helping you to choose a right one.
What is Fiber Attenuator?
Fiber optic attenuator is a passive device used to reduce the power level of an optical signal because too much light can overload a fiber optic receiver and degrade the bit error ratio (BER). To achieve the best BER, the light power must be reduced by using fiber optic attenuator. Generally, the optical attenuators are used in single-mode long-haul applications to prevent optical overload at the receiver.
Optical attenuator reduces signal power by absorbing the light, like sunglasses absorb the extra light energy. Or by scattering the light like an air gap. Fiber optic attenuators are commonly used in two scenarios:
1.Attenuators are permanently installed in a fiber optic links to properly match signal levels at transmitter and receiver.
2.In fiber optic power level testing. Attenuators are used to temporarily add a calibrated amount of signal loss in order to test the power level margins in a fiber optic system.
Types of Fiber Optic Attenuators
Optical attenuator takes a number of different forms. They are typically grouped as fixed optical attenuator and optical variable attenuator.

What is Fixed Fiber Attenuator?
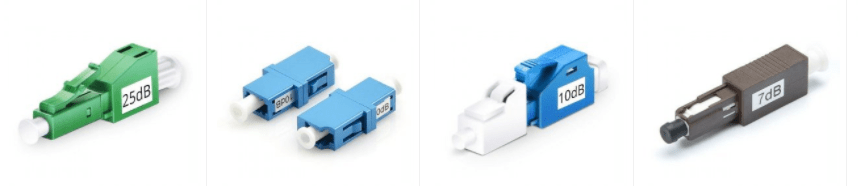
Fixed fiber optic attenuator, also called fixed plug type or fixed build-out fiber attenuator, is used in fiber optic communications to reduce the optical fiber power by a certain level. Typical attenuation values are between 1 and 30 dB. Usually, it has a male plug connector at one side to allow fiber attenuator to be plugged directly into receiver equipment or adapters in patch panel, and has female type fiber optic adapter at the other side to allow the patch cords to plug in. Fixed fiber optic attenuator name is based on the connector type and the attenuation level. LC attenuator 5dB means this attenuator uses LC fiber optic connector, and it can reduce the optical fiber power level by 5dB.
What is optical variable attenuator?
Optical variable attenuator can also be made as a plug-in card. It is a part of Fiber-Mart, all-in-one multi-service transport system. This hot-swappable plug-in variable optical attenuator is an online attenuation adjustment device, only occupying one slot in the 1U/2U/4U chassis. It is applied to applications that optical power required strict control, such as to balance signal strengths in a DWDM network system. Card optical variable attenuator adopts MEMS technology and could continually and variably reduce the light intensity in the optical network and help simulate distance or actual attenuation in the fiber optic testing work. With the card design, this optical variable attenuator is easy to install and remove without any tool. The online attenuation adjustment also contributes to safer business.

How to use Fiber Optic Attenuators in data link?
For a single-mode applications, especially analog CATV systems, the most important parameter, after the correct loss value, is return loss or reflectance. Many types of attenuators (especially gap loss types) suffer from high reflectance, so they can adversely affect transmitters just like highly reflective connectors.

Fiber Optic Attenuator in Data Link
Choose an attenuator with good reflectance specifications, and always install the attenuator ( X in the drawing) at the receiver end of the link as shown above. This is because it’s more convenient to test the receiver power before and after attenuation or while adjusting it with your power meter at the receiver, plus any reflectance will be attenuated on its path back to the source.
Test the system power with the transmitter turned on and the optical attenuator installed at the receiver, and using an optical power meter set to the system operating wavelength. Check to see whether the power is within the specified range for the receiver.
Conclusion
Fiber optic attenuator is an essential passive component in the optical communication system. With the advancement of DWDM technology, as well as the potential to flexibly upgrade the reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer (ROADM), the demand for optical attenuator is sure to soar, especially for optical variable attenuator. The innovation in fiber optic industry never ceases, and fiber optic attenuator will evolve to have lower cost, faster response time and enhanced integration of hybrid with other optical communication devices.Fiber-Mart provides a wide range of fiber optical attenuator.Welcome to contact with us:product@fiber-mart.com.
Knowledge about fiber media converter that you should know
How much do you know about the RJ45 interface?
As we all know, cables can transmit information along their length. To actually get the information where it needs to go, you need to make the right connections to an RJ45 connector. Your cable run needs to terminate into a connector, which needs a jack to plug into. RJ45 is a standard type of connector for network cables, which is usually used for data transmission. RJ45 connectors are most common applications for Ethernet cables and networks.
As we all know, cables can transmit information along their length. To actually get the information where it needs to go, you need to make the right connections to an RJ45 connector. Your cable run needs to terminate into a connector, which needs a jack to plug into. RJ45 is a standard type of connector for network cables, which is usually used for data transmission. RJ45 connectors are most common applications for Ethernet cables and networks.
The RJ45 connector is a modular plug used primarily for network cabling. The connector feature eight pins to which the wire strands of a cable interface electrically. Standard RJ-45 pinouts define the arrangement of the individual wires needed when attaching connectors to a cable.

RJ45 is a type of a variety of different connectors (for example: a type of RJ11 is also a connector, but it is used in the phone). The line using of RJ45 connector has two types: straight-through and cross-over.Have you ever had some confusion about RJ45 interface? That’s what we’ll explore today
Introduction of RJ45 Connector
RJ45 connector is the most common twisted-pair connector for Ethernet cables and networks. “RJ” means “registered jack”, which is a standardized telecommunication network interface for connecting voice and data equipment to a service provided by a local exchange carrier or long distance carrier. The physical connectors that registered jacks use are mainly the modular connector and 50-pin miniature ribbon connector types. RJ45 connector is an 8-position, 8-contact (8P8C) modular plug and jack, which is commonly used to connect computers onto Ethernet-based local area networks (LAN). RJ45 cable plug is usually made of a plastic piece with eight pins on the port. Four of the pins are used for sending and receiving data, and the other four are used for other technologies or power networking devices.

Introduction of RJ45 Connector Color Code
As we all know, there are two wiring schemes: T568A and T568B, which are used to terminate the twisted-pair cable onto the connector interface. Two standards define how the RJ45 pinouts to arrange the individual eight wires when linking RJ45 connector to a cable. These wiring layouts have their own color convention, and following the convention is important to ensure electrical compatibility.
RJ45 Connector VS. RJ11 Connector
Several other types of connectors closely resemble RJ45, and the RJ11 connector used with telephone cables is one of such connectors. The close physical similarity of RJ45 and RJ11 makes it difficult for an untrained eye to tell the two apart. RJ11 connector is a 6P2C (6 position 2 contact) modular connector – only uses six positions rather than eight positions, which make them less popular than RJ45 connectors.
RJ45 and RJ11 are two commonly used jacks, each with their own specific purpose. The biggest difference between them is that they are used for different applications. RJ45 is used in networking, where you connect computers or other network elements to each other. RJ11 is the cable connector that is being used in telephone sets.

Aside from the application, another difference is the number of wires in their connectors. If you look closely at both connectors, you would see that there are only four wires inside an RJ11 while there are eight wires inside an RJ45. As a consequence, RJ45 connector is a little bit bigger than RJ11. It is then quite easy to deduce that you cannot plug in an RJ45 connector to a RJ11 slot but the opposite is possible. Although the smaller size of RJ11 makes it easier to be plugged into the RJ45 slot, it is not recommended to do so since this may damage the device that adopts the RJ45 slot. With proper knowledge and training, some people have been able to use RJ45s all over their house instead of RJ11s.
At present, RJ45 jacks are usually placed on the wall outlets inside people’s houses to reduce the number of visible wiring when using VoIP handsets that are rapidly gaining popularity.
RJ45 type network interface
10/100 Base TX RJ45 interface is commonly used in Ethernet interface, support for network connection speed of 10Base and 100Base of adaptive common RJ45 connector into two categories: for Ethernet cards, routers and Ethernet interface DTE type, for switches DCE type. DTE can be called data terminal equipment; the DCE can be called data communications equipment. In one sense, the DTE device is called the “active communications equipment DCE device called a” passive communications equipment. When the two types of devices use RJ45 interface communication, you must use a crossover cable. This can be defined from the following types of pin definitions of the RJ45 the DTE and RJ45 DCE type pin.
RJ45 type cable plug
The RJ45 network cable connector also known as crystal head which a total of eight cores made of, widely used in LAN and ADSL broadband Internet connection to the user’s cable network equipment which named as CAT cables or twisted-pair. In the specific application, the RJ45-type plugs and cables, there are two connection methods, respectively called T568A line sequence and T568B linear order.

Application in products
RJ45 ports are available on fiber optical products like media converters, pci-e cards, PDH multiplexers, protocol converters, Patch panels, and so on.
Conclusion
RJ45 connectors are the key part of Ethernet connectivity to transmit voice and data media. They were developed as much smaller and cheaper replacements to the older telephone installation methods of hardwired cords. The easy plug-n-play style reduces the difficulty of installation. Compared with RJ11, RJ45 is suitable for more applications, such as Ethernet networking, telecommunications, factory automation and so on. It is frequently used for networking devices including Ethernet cables, modems, computers, laptops, printers, etc.
What is Fiber Optic Adapter
Three connection modes of the switch
There are three main ways to connect switches: cascading, stacking, and clustering. Cascade mode is simple to implement, just an ordinary twisted pair can be, cost savings and basically not limited by the distance. The investment in the stacking method is relatively large and can only be connected within a short distance, which is difficult to achieve. Cluster connection means that multiple interconnected (cascaded or stacked) switches are managed as a logical device.
There are three main ways to connect switches: cascading, stacking, and clustering. Cascade mode is simple to implement, just an ordinary twisted pair can be, cost savings and basically not limited by the distance. The investment in the stacking method is relatively large and can only be connected within a short distance, which is difficult to achieve. Cluster connection means that multiple interconnected (cascaded or stacked) switches are managed as a logical device.

The stacking mode has better performance than the cascaded mode, and the signal is not easily depleted. Through the stacking mode, multiple switches can be managed in a centralized manner, which greatly reduces the management workload. If you really need to use cascading, you can also use the Uplink port. Connection method. Because this can guarantee the signal intensity to the greatest extent, if it is the connection between ordinary ports, it will certainly make the network signal seriously damaged.
1. Switch cascading
This is the most common way to connect multiple switches. It connects through the UpLink on the switch. It should be noted that the switches cannot be cascaded without limitation. Cascading over a certain number of switches will eventually cause broadcast storms, which will lead to a serious drop in network performance. Cascading is further divided into using ordinary port cascading and using Uplink port cascading.

1.1. Use ordinary port cascading
The so-called ordinary port is through a switch of a common port (such as RJ-45 port) to connect.
In the past, it was necessary to use the reverse connection. Now the two ends of the network cable are 568b line sequence. The jumper line is 568a line and 568b line sequence. According to the need, the old version of the device will distinguish the direct line from the crossover line. Now the devices are all common. What kind of consequences, the switch can automatically identify, and only the line can be wrong.
1.2 Use Uplink port cascading
In all switch ports, an Uplink port is included next to it. This port is provided exclusively for upstream connections. Simply connect the port to a port on the other switch except for the “Uplink port” through a straight-through twisted pair (note that it is not the Uplink port that is connected to each other).

2. Switch stack
This type of connection is mainly used in large networks where port requirements are relatively large. The stacking of switches is the quickest and most convenient way to expand ports. At the same time, the bandwidth after stacking is several-tenths of the speed of a single switch port. But not all switches support stacking, depending on whether the switch’s brand or model supports stacking. It is mainly connected through a dedicated connection cable provided by the manufacturer from the “UP” stack port of one switch to the “DOWN” stack port of another switch. All switches in a stack can be managed as a single switch.
Stacked switches are limited by the type and mutual distance. First, the stack switches must support stacking; in addition, the stacked connection cables provided by the manufacturers are generally around 1M, so the stacking function can only be used within a short distance.

3. Cluster
In the so-called cluster, multiple interconnected (cascaded or stacked) switches are managed as a logical device. In a cluster, there is generally only one switch that functions as a management switch,which is called a command switch. It can manage several other switches. In the network, these switches only need to occupy one IP address (only required by the command switch). Under unified management of the command switch, multiple switches in the cluster work together to greatly reduce management intensity.
It should be noted that different manufacturers have different implementations for clusters, and generally manufacturers use proprietary protocols to implement clusters. This determines the cluster technology has its limitations. Switches of different manufacturers can be cascaded but cannot be clustered.
Switching, stacking, and clustering are three different technologies. Cascading and stacking are prerequisites for implementing clusters. Clusters are used for cascading and stacking; cascading and stacking are implemented based on hardware; clusters are implemented based on software; cascading and stacking are sometimes similar (especially cascading and virtual Stacking), sometimes very different (cascade and real stacking).Please feel free to contact Fiber-Mart if you have any needs or questions.we will provide you with the most professional service.