As the infrastructure for access networks, fiber is making rapid headway in the world’s leading technology markets. With passive optical networking (PON) technology gaining popularity, Ethernet passive optical networking (EPON) and igabit passive optical network (GPON) are both in active deployment.
What’s the EPON?
EPON (Ethernet PON) generally delivers 1 Gbit/s symmetrical bandwidth.And its Gigabit Ethernet service actually constitutes 1 Gbit/s of bandwidth for data and 250 Mbit/s of bandwidth for encoding.Employs a single Layer 2 network that uses Internet Protocol (IP) to carry data, voice, and video, generally delivers 1 Gbit/s symmetrical bandwidth.
EPON is a device which serves as the service provider endpoint of apassive optical network. to perform conversion between the electrical signals used by the service provider’s equipment and the fiber optic passive component signals used by the passive optical network. To coordinate the multiplexing between the conversion devices on the other end of that network (called either optical network terminals or optical network units).
What’s the GPON?
GPON, FSAN and ITU have standardized it. Its technical feature is to use ITU-T-defined GFP (General framing procedure) to encapsulate and map multiple services such as Ethernet, TDM and ATM at the second layer, which can provide 1.25Gbps and 2.5Gbps downlink rate, and 155M, 622M, 1.25Gbps, 2.5Gbps several uplink rates, and has a strong OAM function. If you don’t consider EPON, you will see that it will increase to 10Gbps (10G Ethernet is mature). Currently, GPON has advantages in high-speed and multi-service support, but the complexity and cost of technology are currently higher than EPON.
Comparison of EPON and GPON
GPON and EPON Differences
Perhaps the most dramatic distinction between the two protocols is a marked difference in architectural approach. GPON provides three Layer 2 networks: ATM for voice, Ethernet for data, and proprietary encapsulation for voice. EPON, on the other hand, employs a single Layer 2 network that uses IP to carry data, voice, and video.
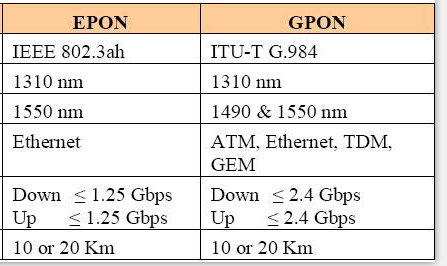
GPON vs EPON: Data Rate
EPON, based on a 10-Gbit/s Ethernet version designated 802.3av. The actual line rate is 10.3125 Gbits/s. The primary mode is 10 Gbits/s upstream as well as downstream. A variation uses 10 Gbits/s downstream and 1 Gbit/s upstream. The 10-Gbit/s versions use different optical wavelengths on the fiber, 1575 to 1580 nm downstream and 1260 to 1280 nm upstream so the 10-Gbit/s system can be wavelength multiplexed on the same fiber as a standard 1-Gbit/s system.
GPON, based on the GPON packets can handle ATM packets directly. Recall that ATM packages everything in 53-byte packets with 48 for data and 5 for overhead. GPON also uses a generic encapsulation method to carry other protocols. It can encapsulate Ethernet, IP, TCP, UDP, T1/E1, video, VoIP, or other protocols as called for by the data transmission. Minimum packet size is 53 bytes, and the maximum is 1518. AES encryption is used downstream only.
Conclusion: GPON is better than EPON
Technology Comparison
EPON, based on Ethernet is the best carrier for carrying IP services; it is easy to maintain, easy to expand, easy to upgrade; EPON equipment is mature and available, EPON has already laid millions of lines in Asia, third-generation commercial chips have been introduced, related optical modules, chip prices Both have dropped significantly, reached the scale of commercial level, and can meet the requirements of recent broadband services; EPON protocol is simple and low in implementation cost, equipment cost is low, and the most suitable technology is needed in the metro access network, not the best technology.
GPON, based on Access network for telecom operation; high bandwidth: line rate, downlink 2.488Gb/s, uplink 1.244Gb/s; high transmission efficiency: 94% (actual bandwidth up to 2.4G) behavior 93% (actual bandwidth up to 1.1) G); business support: G.984.X standard strictly defines the support of carrier-class full service (voice, data and video); strong management capabilities: rich in features, reserved sufficient OAM domain in the frame structure, and The OMCI standard has been developed; the service quality is high: multiple QoS levels can strictly guarantee the bandwidth and delay requirements of the service; the comprehensive cost is low: the transmission distance is long, the split ratio is high, the OLT cost is effectively allocated, and the user access cost is reduced.
Conclusion: As the parts of PON, they have something in common. For example, they both can be accepted as international standards, cover the same network topology methods and FTTx applications, and use WDM (wavelength-division multiplexing) with the same optical frequencies as each other with a third party wavelength; and provide triple-play, Internet Protocol TV (IPTV) and cable TV (CATV) video services
Costs Comparison
PON, as a FTTH technology, is an ideal solution to deliver last-mile broadband access. The optical line terminal (OLT), optical network unit (ONU) and optical distribution network (ODN), which comprise a PON system, decide the costs of GPON and EPON deployments.
The cost of OLT and ONT is influenced by the ASIC (application specific integrated circuit) and optic module. Recently, the chipsets of GPON are mostly based on FPGA (field-programmable gate array), which is more expensive than the EPON MAC layer ASIC. On the other hand, the optic module’s price of GPON is also higher than EPON’s. When GPON reaches deployment stage, the estimated cost of a GPON OLT is 1.5 to 2 times higher than an EPON OLT, and the estimated cost of a GPON ONT will be 1.2 to 1.5 times higher than an EPON ONT.
Conclusion: the cost of EPON and GPON would be the same.
Summary
Currently, we are still unclear whether EPON or GPON will prevail. EPON and GPON have their own advantages and disadvantages. But one thing is clear: PON system is undoubtedly one of the best, EPON and GPON, both technologies have their own advantages, whether it is EPON technology or GPON technology, its application is largely determined by the rapid reduction of fiber access costs and business needs. For more information,welcome to visit www.fiber-mart.com or contact us service@fiber-mart.com