Fiber Optic Connector Types for data center
Important Criteria for Choosing a Datacenter OTDR
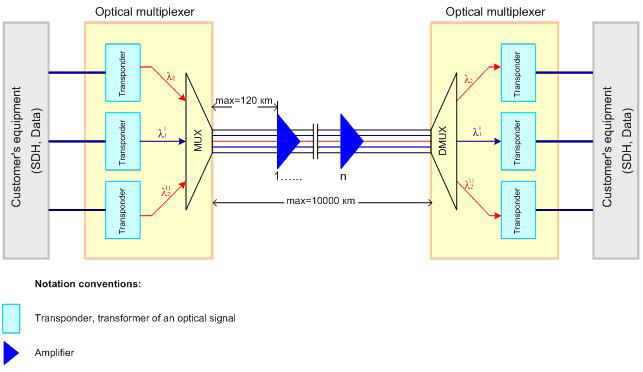
WDM Solution
According to the market demand for large transmission capacity in current optical interconnect,network managers are relying more on fiber optics, and requiring more bandwidth and faster transmission rates over ever increasing distances.
According to the market demand for large transmission capacity in current optical interconnect,network managers are relying more on fiber optics, and requiring more bandwidth and faster transmission rates over ever increasing distances.
What is WDM?
Wavelength Division Multiplexing, WDM, is a technology that increases bandwidth by allowing different data streams at different frequencies to be sent over a single optical fiber network. Signals at WDM wavelengths are independent from each other.
Wave Division Multiplexing (WDM) technologies can increase capacity on the existing fiber infrastructure. WDM is a technology which multiplexes multiple optical signals onto a single fiber by using different wavelengths, or colors, of light. By utilizing WDM communication methods, network managers can realize a multiplicative effect in their available fiber’s capacity.
WDM technology— Short for wavelength division multiplexing, WDM is a way of transmitting multiple simultaneous data streams over the same fiber. Since this happens simultaneously, WDM does not impact transmission speed, latency or bandwidth. WDM functions as multiplexing multiple optical signals on a single fiber by using different wavelengths, or colors, of laser light to carry different signals. Network managers can thus realize a multiplication effect in their available fiber’s capacity with WDM.

Coarse Wave Division Multiplexing (CWDM)
CWDM increases fiber capacity in either 4, 8, or 18 channel increments. It is a method to maximize existing fiber by decreasing the channel spacing between wavelengths. Since CWDM is a passive technology, Another benefit to the passive CWDM technology is that no configuration is necessary, which makes CWDM a low-cost and effortless technology to implement. The most complex step in CWDM integration is aligning and connecting the patch cables from the correct wavelength optic to the correct port on the multiplexers on each end of the link.
The benefits of CWDM include:
- Passive equipment that uses no electrical power
- Extended Temperature Range (0˚C – 70˚C)
- Lower cost per channel than DWDM
- Scalability to grow fiber capacity with little or no increased cost
- Protocol transparent
- Simple to install and use
Drawbacks of CWDM:
- 18 channels may not be enough, and fiber amplifier cannot be used with them
- Passive equipment that has no management capabilities
- Not the ideal choice for long-haul networks
Dense Wave Division Multiplexing (DWDM)
Dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) is a technology that puts data from different sources together on an optical fiber, with each signal carried at the same time on its own separate light wavelength. Using DWDM, is a layer-1 transport technology that multiplexes several optical signals into the same fiber by using different wavelengths (colors). It allows you to transport more data across existing dark fiber infrastructure.up to 80 (and theoretically more) separate wavelengths or channels of data can be multiplexed into a light-stream transmitted on a single optical fiber.
Benefits of DWDM:
- Transparency: due to that DWDM is with a physical layer architecture, it can transparently support both TDM and data formats such as ATM, Gigabit Ethernet, ESCON, and Fibre Channel with open interfaces over a common physical layer.
- Scalability: DWDM can leverage the abundance of dark fiber in many metropolitan area and enterprise networks to quickly meet demand for capacity on point-to-point links and on spans of existing SONET/SDH rings.
- Dynamic provisioning: fast, simple, and dynamic provisioning of network connections give providers the ability to provide high-bandwidth services in days rather than months.
Drawbacks of DWDM:
- DWDM solutions are quite expensive
- Active DWDM solutions require a lot of set-up and maintenance expense
CWDM Mux / Demux
Using CWDM multiplexing technology paired with wavelength specific optics in Transition Networks’ fiber optic devices and switching products allows you to realize the full benefit of CWDM technology. The modular approach that Transition Networks takes toward CWDM deployments makes scaling a project to fit your exact needs easy and affordable. Transition Networks also offers products that optimize standard fixed optic wavelengths on existing products by converting them to the appropriate CWDM “color” or wavelength.
DWDM Mux / Demux
the common configuration of DWDM Mux/Demux is from 8 to 96 channels. Maybe in future channels can reach 200 channels or more. DWDM system typically transports channels (wavelengths) in what is known as the conventional band or C band spectrum, with all channels in the 1550nm region. The denser channel spacing requires tighter control of the wavelengths and therefore cooled DWDM optical transceiver modules required, as contrary to CWDM which has broader channel spacing un-cooled optics, such as CWDM SFP, CWDM XFP.
To sum it up, With DWDM Mux/DeMux, single fibers have been able to transmit data at speeds up to 400Gb/s. there is no doubt that DWDM technology will reshape the future communication network by virtue of its various advantages and applications in many aspects.To expand the bandwidth of your optical communication networks with lower loss and greater distance capabilities.
WDM solution capacity expansion in a more cost-effective, simplified and flexible way.Fiber-MART can help you to choose the right WDM solution.Any question pls feel free to contact us .E-mail: Service@fiber-mart.com
Introduction of Loopback Cable and How do we Create it?
A loopback cable is also known as loopback plug or loopback adapter, which is a plug used to test physical ports to identify network issue. It provides system test engineers a simple but effective way of testing the transmission capability and receiver sensitivity of network equipment.
In our day to day jobs we find ourselves lugging around more and more hardware; pda, laptop, cell phone, and sometimes even hubs. Why do we carry a hub around when sometimes all we need is a link on our ethernet cards so that all the applications on the system work. Yes, I know you could setup a loopback software adapter. But if you are looking to have the system configured as close to the real setup as possible and you don’t want to carry a hub around, just to get a link light on your NIC. Consider building yourself a loopback cable.

What Is Loopback Cable?
A loopback cable is also known as loopback plug or loopback adapter, which is a plug used to test physical ports to identify network issue. It provides system test engineers a simple but effective way of testing the transmission capability and receiver sensitivity of network equipment. In a word, it is a connection device that is plugged into a port to perform a loopback test. There are loopback plugs for many different ports, including serial ports, Ethernet ports, and WAN connections.
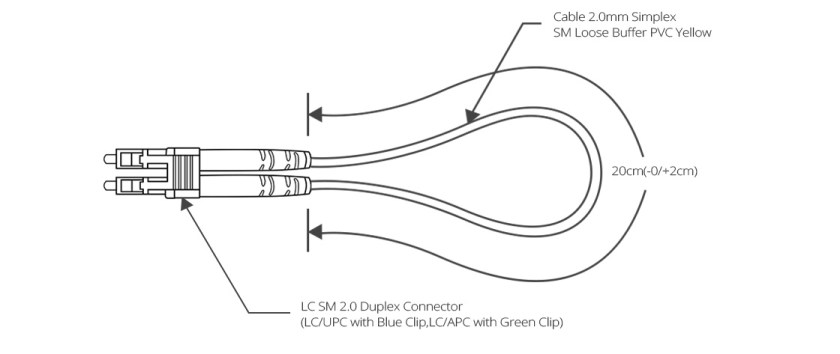
Loopback Cable Type
Fiber Loopback Cable
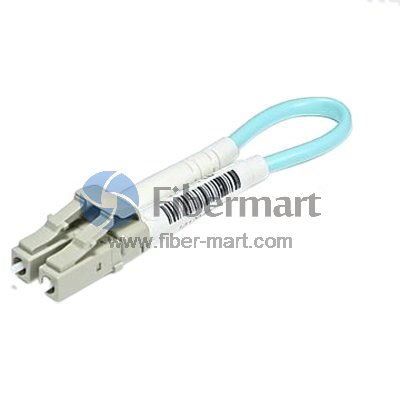
Fiber optic loopback incorprates two fiber optic connectors which are plugged into the output and input port of the equipment respectively. Therefore, fiber loopback cables can be classified by the connector types, such as LC, SC, FC, MTRJ. These fiber optic loopback plug connectors are compliant to IEC, TIA/EIA, NTT and JIS specifications. Besides, fiber optic loopback cables also can be divided into single mode and multimode fiber loopback. To describe this item clearly, I will take LC fiber optic loopback cable as an example, which is one of the most popular cables (as shown in the following figure). The LC fiber optic loopback cables support the test of transceivers featuring LC interface. They can comply with the RJ-45 style interface with low insertion loss, low back reflection and high precision alignment. LC loopback cables can be 9/125 single mode, 50/125 multimode or 62.5/125 multimode fiber type.

RJ45 Loopback Cable
A Gigabit RJ45 loopback cable is an exceedingly user friendly cable tester. It looks like a simple plug at first glance, but the compact and rugged design makes it highly portable and usable in the tightest corners. All you have to do is to simply plug the Gigabit RJ45 loopback into the jack that you want to test or the one you are suspicious about. If the link LED on your switch is active, it means that the connection is operating perfectly. The RJ45 loopback cable will negate the necessity to carry a bulky network hub around.

How to build the loopback cable simplified?
If you are handy with building ethernet cables, the simple explanation is;
- Redirect Pin 1 to Pin 3 and Pin 2 to Pin 6.
- Make sure you create tight twists to account for signal interference at such a short length.

How to build a loopback cable illustrated?
Step 1. Get a pair of approximately 4 inches in length of cat 5 cable.
Step 2. Leave approximately 1/2 inch at end and start twisting, very tightly.
Note: If your fingers start to hurt, you may want to use a tool to help with the twisting. Notice how tightly wound the cable is. If the twists are not close enough the loopback will not work. Please twist to match picture.
Step 3. After twisting is done, fold cable and line up the ends. Cut if you must to line up cables. Line up the cables so that the cables are in the proper alignment to prepare for insertion into RJ-45 end.
Step 4: Insert cable into RJ-45 end. (do not crimp yet.) Remember, 1236 pins.
Step 5. Insert plastic tubing over the wire and into the RJ-45 end. Now crimp the end with a crimping tool.
Note: When you first plug in the loopback cable, wait approximately 10 seconds to get a link light. No more carrying around a hub just to get a link light.

Conclusion
All in all, If we know what a is loopback cables and know how to create loopback cables, it will bring many benefits to our work and life.loopback cables play an important role in troubleshooting in laboratories and manufacturing environments. They facilitate the testing of simple networking issues and are available at very low costs. There are many loopback cable manufactures on the market, providing single mode and multimode fiber optic loopback plugs available with FC, LC, MT-RJ, SC connectors. Fiber-Mart is one of the fiber loopback cable providers, all loopback cables are precision terminated and feature extremely low loss characteristics for transparent operation in the test environment.
Cable Management Procedures


