Category: Fiber Transceivers
Optical transceivers, Active Optic Cables, data center switches, and cable management in data centers.
NEW GENERATION 100G WDM NETWORK TECHNOLOGY
How to choose the basic 40G QSFP + optical components ?
With high-speed development of the optical communication industry,why is the third-party 40G QSFP with good compatibility and high stability the perfect choice for customers?
With high-speed development of the optical communication industry,why is the third-party 40G QSFP with good compatibility and high stability the perfect choice for customers?
40G LR4 QSFP+ Transceiver
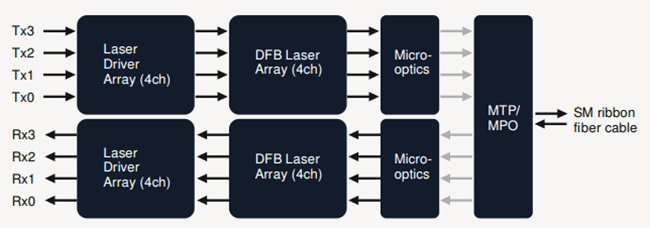
Conforming to the 802.3ba (40GBASE-LR4) standard, the 40G LR4 QSFP+ transceiver together with the LC connector can support an optical link length up to 10 kilometers over single mode fiber. 40G LR4 QSFP+ transceivers offer 4 independent transmit and receive channels. And to realize the function of transmitting the 4-channel signals over the single mode fiber, this kind of transceiver has to introduce MUX/DEMUX to multiplex/de-multiplex optical signals.the working principle of this kind of QSFP+ transceiver is : In the transmit side, four 10 Gbp/s serial data streams are passed to laser drivers. The laser drivers control directly modulated lasers (DMLs) with wavelengths. the output of the four DMLs are optically multiplexed to a single-mode fiber through an industry-standard LC connector. In the receive side, the four 10 Gbp/s optical data streams are optically de-multiplexed by the integrated optical demultiplexer; then, each data steam is recovered by a PIN photodetector/transimpedance amplifier and passed to an output driver. The following figure shows the functional block diagram of the 40G LR4 QSFP+ transceiver.
40G SR4 QSFP+ Transceiver
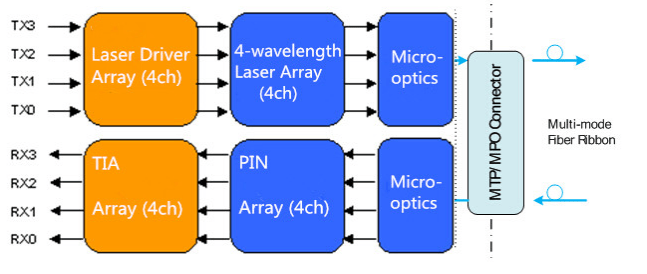
40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+, Short-reach (SR) transceivers for 40G connectivity in a QSFP form factor, uses independent transmitter and receiver sections, each with 4 parallel fiber strands. It can transmit 150 meters over OM4 MMF. For a 40G connection, 8 fiber strands are required, and 12-fiber MPO connectors are used. Consequently, 4 fiber strands in each connection are wasted .For most data center networks, the aggregation-layer fiber infrastructure is built for 10G connectivity. That either supports direct connections between devices over LC-to-LC MMF, or uses LC-to-LC fibers to attach devices to patch panels. Regular duplex LC-to-LC fibers cannot be directly reused for 40G connectivity using traditional 40G transceivers.The operating principle of the 40G SR4 QSFP+ Transceiver is : the transmitter converts parallel electrical input signals into parallel optical signals through the use of a laser array. Then the parallel optical signals are transmitted parallelly through the multimode fiber ribbon. Reversely, the receiver converts parallel optical input signals via a photo detector array into parallel electrical output signals. The following figure shows the functional block diagram of the 40G SR4 QSFP+ Transceiver.
Features of OEM 40G QSFP Transceiver Modules
As we know, the OEM 40G QSFP transceiver from name brand like Cisco, Juniper and Brocade is widely used in data center and enterprise network. They all have some great features. The Cisco 40G QSFP transceiver offers a wide variety of high-density and low-power 40 Gigabit Ethernet connectivity options for data center, high-performance computing networks, enterprise core and distribution layers, and service provider applications. Here are some benefits of Cisco 40 Gbps transceiver:
- Hot-swappable input/output device that plugs into a 40 Gigabit Ethernet Cisco QSFP port
- Flexibility of interface choice (for different reach requirements and fiber types)
- Interoperable with other IEEE-compliant 40GBASE interfaces where applicable
- Certified and tested on Cisco QSFP 40G ports for superior performance, quality, and reliability
- High-speed electrical interface compliant to IEEE 802.3ba
- QSFP Form factor, 2-wire I2C communication interface and other low-speed electrical interface compliant to SFF 8436 and QSFP
- The Brocade 40 Gbps transceiver supports highly reliable operations in data center and is optimized for Brocade switching platforms. It undergoes strict qualification and certification testing.
Conclusion
For the 40 Gbps transceiver, Fiber-MART provides high quality QSFP+ transceivers and various of compatible brands for you, Cisco, Genetic, Juniper Networks, Arista Networks, Brocode, HPE, Dell, Intel, IBM, etc. All have passed the compatibility testing. and the prices are much lower than other vendors,if you any question pls feel free to contact me .E-mail :service@fiber-mart.com
TIPS TO CLEAN FIBER OPTIC CONNECTORS
SOMETHING YOU SHOULD KNOW BEFORE USING FIBER OPTIC JUMPER
CHOOSING FIBER OPTIC CABLE OR COPPER WIRE FOR COMMUNICATION
