Author: Fiber-MART.COM
How to Clean and Connecting Optical Fibers to OTDR
OTDR FAQ, for all kinds of OTDR
How to choose 3G Digital Video SFP ?
In fiber optic network industry, Digital video SFP is responsible for transmitting HD or higher standard video.
In fiber optic network industry, Digital video SFP is responsible for transmitting HD or higher standard video, so there are 3G digital video SFPs suitable for SD/HD/3G-SDI. and so more and more people are interested in SFP modules.
What is SDI?
Digital Video SFP is a 3G-SDI standard optical transceiver designed to transmit SDI, HD-SDI, or DVB digital video signals over fiber. It is a dual channel optical transmitter module which transmits optical serial digital signals that defined in SMPTE 297-2006.

Fiber Optic Transport of HD/SD-SDI It is becoming increasingly necessary and economically feasible to transport HD/SD-SDI signals over fiber instead of coaxial cable. SDI, the abbreviation for Serial Digital Interface, is a digital video interface standard made by SMPTE organization. This serial interface transmits every bit of data word and corresponding data through single channel. Due to the high data rate of serial digital signal(a kind of digital baseband signal), it must be processed before transmission.Additional SDI standards include HD-SDI, 3G-SDI, 6G-SDI, and 12G-SDI. HD-SDI was standardized by SMPTE 372M in 1998. It can support 1.485Gbps interface. 3G-SDI consists of a single 2.970Gbps serial link that allows replacing dual link HD-SDI.
3G Digital Video SFPs Types
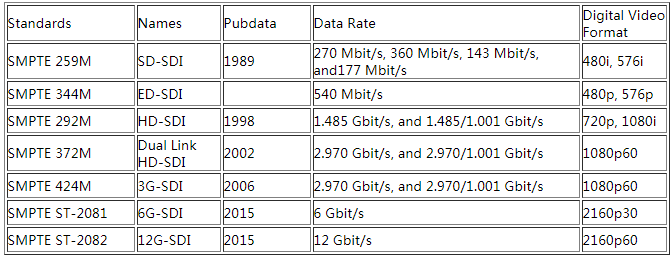
3G digital video SFPs include 3G SDI SFP, BiDi SFP and CWDM SFP. According to different standards, it can be divided into different types. Based on the transmission mode, it can be divided into single Tx, single Rx, dual Tx, dual Rx and TR transceivers; by standards into MSA and non-MSA; by operating wavelength into 1310nm, 1490nm, 1550nm and CWDM wave length.It also exists video modules of electrical interfaces that adapting mini BNC port to coordinate with SFP slot-supporting digital matrix. Currently there are also on the market some crossover video transceivers, for example, transfer the encoded SG-SDI to IP protocol conversion module can be used in traditional Ethernet switch, replacing video codec equipment. 3G digital video SFPs also have 3G video SFP and 3G video pathological patterns due to different applications.the data rate of digital SDI as below.
Now we say that what are 3G-SDI pathological patterns? Pathological patterns, also called SDI proving ground, are a whole test signal. And it must be done during blackout. This signal is tough to handle by serial digital system, and significant to check the system performance. Pathological patterns often contain the richest low-frequency energy which statistically happens one per frame. Pathological patterns test is also an important indicator of video SFP modules. Fiber-Mart provides a series of 3G-SDI SFP modules to support transmission rates from 50 Mbps to 3 Gbps. These digital video modules are specifically designed for SMPTE SDI pathological patterns, allowing hot-plug capability with the 20-pin SFP connectors.
According to this article, i believe you have known some knowledges about 3G Digital Video SFP. Fiber-MART can provide you custom service and a series of 3G-SDI SFP modules to support transmission rates from 50 Mbps to 3 Gbps. Any question pls not hesitate to contact us.E-mail:service@fiber-mart.com
Five things you should know before your next installation
MPO/MTP Trunk Cable Advantages

