Author: Fiber-MART.COM
FIBER OPTIC CONNECTORS: THEN VS. NOW
5 FACTS ABOUT YOUR FIBER OPTIC CABLE CONNECTION CLEANLINESS
Maintaining clean fiber optic cable connections is a vital part of any network installation, but proper cleaning is often overlooked. Check out the 5 facts below, and then make sure you think twice before making a connection without ensuring that your connector’s end faces are clean:
#1 – IMPROPER CLEANING OF FIBER OPTIC CABLE CONNECTIONS
How to Place EDFA for DWDM Distance Extension?
No matter where the EDFA optical amplifier is deployed in the DWDM link, the signal power can be always enhanced for making a longer DWDM system.Undoubtedly, the EDFA amplifier is an ideal choice for long-haul DWDM system. But how does it work for extending DWDM system?
No matter where the EDFA optical amplifier is deployed in the DWDM link, the signal power can be always enhanced for making a longer DWDM system.Undoubtedly, the EDFA amplifier is an ideal choice for long-haul DWDM system. But how does it work for extending DWDM system?
Optic Amplifier Basics
The basic form of EDFA consists of a length of EDFA, a pump laser, and a WDM system for combining the signal and pump wavelength so that they can propagate simultaneously through the EDF.
When transmitting over long distance, the optical signal has to be amplified many times in between owing to the signal loss from fiber attenuation, connectivity losses, fiber splicing losses, etc. Before optical amplifier is invented, the optical signal has to be first converted into electrical signal, amplified, and then converted back to optical signal again. The process is very complicated and expensive. Optical amplifier has since been invented that can amplify signals directly, this process is significantly cheaper and started a fiber optic revolution. There are three fiber optic amplifier types: EDFA, Raman amplifier and semiconductor optical amplifier(SOA).
EDFA (Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier) principle
EDFAs use a pump laser (980 nm or 1480 nm) to bring up electrons to a higher energy level. If signal amplification is achieved by emitted photons of the same signal wavelength with the help of stimulated emission.

An erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) is a device that amplifies an optical fiber signal. It is used in the telecommunications field and in various types of research fields. An EDFA is “doped” with a material called erbium. The term “doping” refers to the process of using chemical elements to facilitate results through the manipulation of electrons.The EDFA was the first successful optical amplifier and a significant factor in the rapid deployment of fiber optic networks during the 1990s.
The EDFA rate, or amplification window, is based on the optical wavelength range of amplification and is determined by the dopant ions’ spectroscopic properties, the optical fiber glass structure and the pump laser wavelength and power. As ions are sent into the optical fiber glass, energy levels broaden, which results in amplification window broadening and a light spectrum with a broad gain bandwidth of fiber optic amplifiers used for wavelength division multiplex communications. This single amplifier may be used with all optic fiber channel signals when signal wavelengths are in the amplification window. Optical isolator devices are placed on either side of the EDFA and serve as diodes, which prevent signals from traveling in more than one direction.
How Does EDFA Amplifier Work?
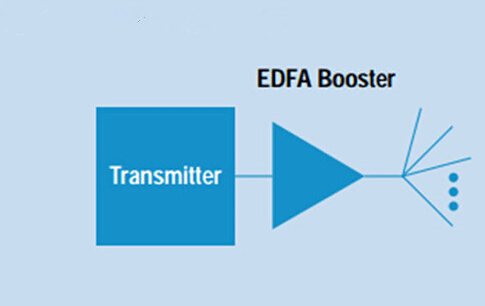
Placed at the Transmitting Side : A booster optical amplifier operates at the transmission side of the link, working to amplify aggregated optical input power for reach extension. Booster EDFA is designed to enhance the transmitted power level or to compensate for the losses of optical elements between the laser and optical fibers. It is usually adopted in a DWDM network where the multiplexer attenuates the signal channels. Booster optical amplifier features high input power, high output power, and medium optical gain.
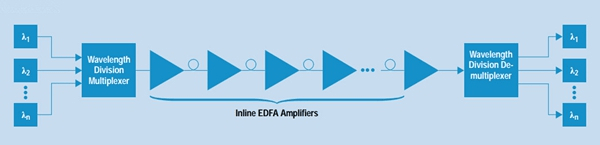
Placed at the Intermediate Points: as shown in the figure below, the EDFA in-line amplifier can be put at any intermediate point along the long transmission link. This kind of EDFA optical amplifier is designed with low input power, high output power, high optical gain and low noise figure, which are normally deployed every 80-100 km to amplify signals between any two link nodes on the main optical link, with the aim of compensating the loss caused by fiber transmission and other factors. Thereby, the optical signal level can stay above the noise floor.
Placed at the Receiving Side: A pre-amplifier operates at the receiving end of a DWDM link. Pre-amplifiers are used for optical amplification to compensate for losses in a demultiplexer located near the optical receiver. Placed before the receiver end of the DWDM link, pre-amplifier works to enhance the signal level before the photo detection takes place in an ultra-long haul system, hence improving the receive sensitivity. It features medium to low input power, medium output power, and medium gain.

Conclusion
The EDFA optical amplifier can be deployed as booster optical amplifier , in-line amplifier and pre-amplifier contributes to optimize network performance for extending the reach. It can also work as in-line amplifier at the intermediate point along the link for compensating the fiber loss in the transmission link.Which also increases data capacity required for current and future optical communication system. Optical Amplifiers provided by Fiber-Mart are designed for all network segments (access, metro, regional and long haul) and applications (telecom, cable and enterprise). any question pls not hesitate to contact us www.fiber-mart.com or E-mail: service@fiber-mart.com
Introduction of Armored fiber cable
Introduction to Passive Optical Network (PON)
Seen from the entire network structures,the Passive Optical Network (PON) market is in a high-growth period due to the ongoing deployments of Fiber to the Home (FTTH) networks.today, we mainly Introduce Passive Optical Network (PON).
What does Passive Optical Network (PON)mean?
A passive optical network (PON) is a cabling system that uses optical fibers and optical splitters to deliver services to multiple access points. A PON system can be fiber-to-the-curb (FTTC), fiber-to-the-building (FTTB) or fiber-to-the-home (FTTH). A PON system consists of optical line termination (OLT) at the communication provider’s end and a number of optical network units (ONUs) at the user’s end. The term “passive” simply means that there are no power requirements while the network is up and running.
A PON consists of an optical line terminal (OLT) at the service provider’s central office (hub) and a number of optical network units (ONUs) or optical network terminals (ONTs), near end users. A PON reduces the amount of fiber and central office equipment required compared with point-to-point architectures. A passive optical network is a form of fiber-optic access network.In most cases, downstream signals are broadcast to all premises sharing multiple fibers. Encryption can prevent eavesdropping.upstream signals are combined using a multiple access protocol, usually time division multiple access (TDMA).
Feature
A PON takes advantage of wavelength division multiplexing (WDM), using one wavelength for downstream traffic and another for upstream traffic on a single mode fiber (ITU-T G.652). BPON, EPON, GEPON, and GPON have the same basic wavelength plan and use the 1490 nanometer (nm) wavelength for downstream traffic and 1310 nm wavelength for upstream traffic. most common is 28 dB of loss budget for both BPON and GPON, but products have been announced using less expensive optics as well. 28 dB corresponds to about 20 km with a 32-way split. Forward error correction (FEC) may provide for another 2–3 dB of loss budget on GPON systems. As optics improve, the 28 dB budget will likely increase. Although both the GPON and EPON protocols permit large split ratios (up to 128 subscribers for GPON, up to 32,768 for EPON), in practice most PONs are deployed with a split ratio of 1:32 or smaller.
A PON consists of a central office node, called an optical line terminal (OLT), one or more user nodes, called optical network units (ONUs) or optical network terminals (ONTs), and the fibers and splitters between them, called the optical distribution network (ODN). “ONT” is an ITU-T term to describe a single-tenant ONU. In multiple-tenant units, the ONU may be bridged to a customer premises device within the individual dwelling unit using technologies such as Ethernet over twisted pair, G.hn (a high-speed ITU-T standard that can operate over any existing home wiring – power lines, phone lines and coaxial cables) or DSL. An ONU is a device that terminates the PON and presents customer service interfaces to the user. Some ONUs implement a separate subscriber unit to provide services such as telephony, Ethernet data, or video.
An OLT provides the interface between a PON and a service provider′s core network. These typically include:
- IP traffic over Fast Ethernet, gigabit Ethernet, or 10 Gigabit Ethernet;
- Standard TDM interfaces such as SDH/SONET;
- ATM UNI at 155–622 Mbit/s.
functions are separated into two parts:
- The ONU, which terminates the PON and presents a converged interface—such as DSL, coaxial cable, or multiservice Ethernet—toward the user;
- Network termination equipment (NTE), which inputs the converged interface and outputs native service interfaces to the user, such as Ethernet and POTS.
The Benefits of PON
As early as before, PONs began appearing in corporate networks. Users were adopting these networks because they were cheaper, faster, lower in power consumption, easier to provision for voice, data and video, and easier to manage, since they were originally designed to connect millions of homes for telephone, Internet and TV services.Passive Optical Networks (PON) provide high-speed, high-bandwidth and secure voice, video and data service delivery over a combined fiber network.
The main benefits of PON as below:
- Lower network operational costs
- Elimination of Ethernet switches in the network
- Elimination of recurring costs associated with a fabric of Ethernet switches in the network
- Lower installation (CapEx) costs for a new or upgraded network (min 200 users)
- Lower network energy (OpEx) costs
- Less network infrastructure
- You can reclaim wiring closet (IDF) real estate
- Large bundles of copper cable are replaced with small single mode optical fiber cable
- PON provides increased distance between data center and desktop (>20 kilometers)
- Network maintenance is easier and less expensive
Conclusion
According to the above article, you may have a understanding of the passive optical network.A PON network eliminates the need for switches and a wiring closet, which means fewer points of failure. Fiber-Mart manufactures and offers customized services. any question pls welcome to visit http://www.fiber-mart.com or contact us.E-mail: service@fiber-mart.com

