As we know, in most cases, when a fiber is used or spliced, it is essential to prepare clean ends. Stripping, cleaving, polishing are the basic steps to ensure fiber ends clean and smooth. Cleaving, an essential step of making fiber ends clean, though it’s a simple mean, but it works surprisingly well, at least for standard glass fibers. Thus, I want to share something about the cleaving in this paper today.

Basics of Fiber Optic Cleaving
Fiber optic cleaving is one of the several processes in the preparation for a fiber splice operation. The purpose of cleaving is to prepare the end of the fiber so that it makes a very nearly perfect right angle with the body of the fiber and that this end face is nearly perfectly smooth. With a well-performed cleaving operation, a clean and flat endface was created perpendicular to the length of the fiber, with no protruding glass on either end. Besides it can also help to achieve a successful low loss splice of an optical fiber.
The technique of Fiber Optic Cleaving
A general strategy involved in the technique of fiber optic cleaving is known as the scribe-and-tension or scribe-and-break strategy. With the use of cutting tool made from materials such as diamond, sapphire or tungsten carbide, this process involves the introduction of a crack in the fiber, then followed by the application of tensile stress in the vicinity of the crack.
However, the specific implementations of the cleaving can be various thus lead to cleaves of different qualities. Some implementations may apply the tensile force uniformly across the cross section of the fiber while others might bend the fiber around a curved surface, causing excessive tensile stress on the outside of the bend. Besides, the crack in the fiber may also be generated in different ways: the crack may be introduced at a single point on the circumference or it may be generated all along the circumference of the fiber prior to the application of the tensile force. The circumferential introduction of the crack often allows fibers of considerably large diameters to be cleaved while maintaining high quality of the cleave.

Two Types of Fiber Optic Cleavers
As mentioned before, fiber optic cleavers can be classified into precision cleavers and cheap or scribe cleavers.
Scribe Cleavers—The scribe or manual cleaver, which is cheaper than the precision cleaver, is the most original type of fiber optic cleaver. Scribe cleavers are usually shaped like ballpoint pens with diamond tipped wedges or come in the form of tile squares. The scribe has a hard and sharp tip, generally made of carbide or diamond, to scratch the fiber manually. Then the operator pulls the fiber to break it. Since the breaking process is under manual control, it is hard to control the force, which makes the cleaving less accurate and precise. That’s why most technicians shy away from these cheap cleavers.
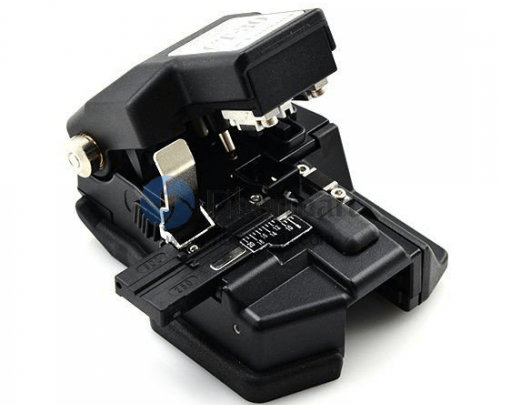
Precision Cleavers—As the name implies, precision cleavers can do a preciser cleaving job compared to the scribe cleavers. A precision cleaver uses a diamond or tungsten wheel/blade to provide the nick in the fiber. Tension is then applied to the fiber to create the cleaved end face. The advantage of the precision cleavers is that they can produce repeatable results through thousands of cleaves by simply just rotating the wheel/blade accordingly. Although they are more costly than scribe cleavers, precision cleavers can cut multiple fibers with increasing speed, efficiency, and accuracy. As the fusion splicers became popular, precision cleavers were developed to support various splicing works. Precision cleavers are deal for fusion splicing standard 125/250um & 125/900um fibers and preparing fiber for various pre-polished connectors.
Operation Procedure for Fiber Cleavers
A fiber cleaver utilizes an automatic anvil drop for fewer required steps and better cleaving consistency. The automated anvil design can save time and significantly improve the quality of the cleave by eliminating human error and subpar cleaves associated with scribes and manual cleavers. To perfectly cleave optical fibers, perform the following steps:
Step 1: Open the body cover and put the stripped fiber on the v-groove.
Step 2: Close the holder cover.
Step 3: Close the cover and move the slider forward to cleave the fiber.
Step 4: Open the cover and check the cleaved fiber.
Step 5: Open the holder cover and take out the cleaved fiber.
Step 6: Remove the chip of cleaved fiber with a pair of tweezers.

Tips on Choosing Fiber Cleavers
1.Select fiber cleavers according to your application requirements. Fiber cleavers, designed for fusion splicing, need a low average angle that is one degree or less, whereas cleavers appropriate for mechanical connectors require angles below three degrees. So determine whether you require a single-fiber or multi-fiber cleaver before you cleave the fibers at one time.
2.Think twice before purchasing a cleaver built into a splicer. If you intend to purchase the built-in cleavers, you must check whether the cleaver or splicer requires maintenance. It may cause inconvenience to technician if they loses valuable tools, which can hold up the job at hand.
3.Purchase a cleaver with the latest automation features that can save a lot of labour and time. Fiber cleavers are always continuing to evolve with new and improved features, such as automated fiber scrap collection, automated scoring mechanisms, and the latest automatic blade rotation technology.
Conclusion
To get good fiber optic splices or terminations, especially when using the pre-polished connectors with internal splices, it is extremely important to cleave the fiber properly. As we know, fiber splicing requires mating two fiber ends. Any defect of the ends would impact the performance of fiber splicing.To buy reliable and high precision fiber cleavers, please visit www.fiber-mart.com or contact us product@fiber-mart.com.