Do you know what is the fiber attenuator used for? As we know, the source of the single mode fiber is laser, the power of which is extremely strong. Therefore we can use single mode fiber to achieve long distance transmission. But, if the transmission distance over single mode fiber is too short, too much light may overload a fiber optic receiver, which may cause serious high bit error rates. How to solve this? Fiber attenuator should be inserted at the receiver end to reduce the power to the proper level. This article sheds light on types, and applications of optical attenuators, helping you to choose a right one.
What is Fiber Attenuator?
Fiber optic attenuator is a passive device used to reduce the power level of an optical signal because too much light can overload a fiber optic receiver and degrade the bit error ratio (BER). To achieve the best BER, the light power must be reduced by using fiber optic attenuator. Generally, the optical attenuators are used in single-mode long-haul applications to prevent optical overload at the receiver.
Optical attenuator reduces signal power by absorbing the light, like sunglasses absorb the extra light energy. Or by scattering the light like an air gap. Fiber optic attenuators are commonly used in two scenarios:
1.Attenuators are permanently installed in a fiber optic links to properly match signal levels at transmitter and receiver.
2.In fiber optic power level testing. Attenuators are used to temporarily add a calibrated amount of signal loss in order to test the power level margins in a fiber optic system.
Types of Fiber Optic Attenuators
Optical attenuator takes a number of different forms. They are typically grouped as fixed optical attenuator and optical variable attenuator.

What is Fixed Fiber Attenuator?
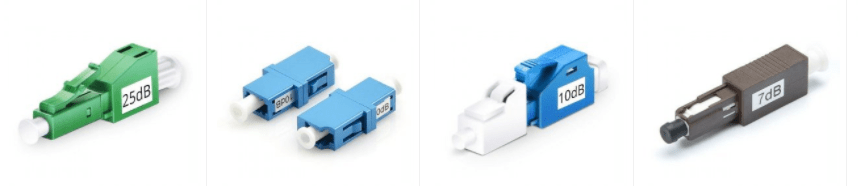
Fixed fiber optic attenuator, also called fixed plug type or fixed build-out fiber attenuator, is used in fiber optic communications to reduce the optical fiber power by a certain level. Typical attenuation values are between 1 and 30 dB. Usually, it has a male plug connector at one side to allow fiber attenuator to be plugged directly into receiver equipment or adapters in patch panel, and has female type fiber optic adapter at the other side to allow the patch cords to plug in. Fixed fiber optic attenuator name is based on the connector type and the attenuation level. LC attenuator 5dB means this attenuator uses LC fiber optic connector, and it can reduce the optical fiber power level by 5dB.
What is optical variable attenuator?
Optical variable attenuator can also be made as a plug-in card. It is a part of Fiber-Mart, all-in-one multi-service transport system. This hot-swappable plug-in variable optical attenuator is an online attenuation adjustment device, only occupying one slot in the 1U/2U/4U chassis. It is applied to applications that optical power required strict control, such as to balance signal strengths in a DWDM network system. Card optical variable attenuator adopts MEMS technology and could continually and variably reduce the light intensity in the optical network and help simulate distance or actual attenuation in the fiber optic testing work. With the card design, this optical variable attenuator is easy to install and remove without any tool. The online attenuation adjustment also contributes to safer business.

How to use Fiber Optic Attenuators in data link?
For a single-mode applications, especially analog CATV systems, the most important parameter, after the correct loss value, is return loss or reflectance. Many types of attenuators (especially gap loss types) suffer from high reflectance, so they can adversely affect transmitters just like highly reflective connectors.

Fiber Optic Attenuator in Data Link
Choose an attenuator with good reflectance specifications, and always install the attenuator ( X in the drawing) at the receiver end of the link as shown above. This is because it’s more convenient to test the receiver power before and after attenuation or while adjusting it with your power meter at the receiver, plus any reflectance will be attenuated on its path back to the source.
Test the system power with the transmitter turned on and the optical attenuator installed at the receiver, and using an optical power meter set to the system operating wavelength. Check to see whether the power is within the specified range for the receiver.
Conclusion
Fiber optic attenuator is an essential passive component in the optical communication system. With the advancement of DWDM technology, as well as the potential to flexibly upgrade the reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer (ROADM), the demand for optical attenuator is sure to soar, especially for optical variable attenuator. The innovation in fiber optic industry never ceases, and fiber optic attenuator will evolve to have lower cost, faster response time and enhanced integration of hybrid with other optical communication devices.Fiber-Mart provides a wide range of fiber optical attenuator.Welcome to contact with us:product@fiber-mart.com.