Fiber optic cable, which is lighter, smaller and more flexible than copper, can transmit signals with faster speed over longer distance. However, many factors can influence the performance of fiber optic transmission. Losses in optical fiber are negligible issues among them, and it has been a top priority for every engineer to work with and figure out solutions for.
Light traveling in an optical fiber loses power over distance. The loss of power depends on the wavelength of the light and on the propagating material. For silica glass, the shorter wavelengths are attenuated the most (see Fig. 1). The lowest loss occurs at the 1550-nm wavelength, which is commonly used for long-distance transmissions.

Transmission of light by fibre optics is not 100% efficient. There are several reasons for this including absorption by the core and cladding (caused by the presence of impurities) and the leaking of light from of the cladding. When light reflects off the cladding /core interface it actually travels for a short distance within the cladding before being reflected back. This leads to attenuation (signal reduction) by up to 2db/Km for a multi-mode fibre. For example, with this level of attenuation, if light travelled over 10kM of cable only 10% of the signal would arrive at the following end.
The amount of attenuation for a given cable is also wavelength dependent. Figure 1 shows the attenuation profile for the two main types of fibre; multi-mode and single-mode cable (described in detail below). The absorption peak at 1000nm is caused by the peculiarities of single mode fibre while the peak at 1400nm is caused by traces of water remaining in the fibre as an impurity. Due to this water absorption peak there are two standard single-mode wavelengths in use, 1310nm and 1550nm. 1310nm has been a standard for many years, only now is there a trend towards using 1550nm brought about by the need to extend the distances between repeaters.
The loss of power in light in an optical fiber is measured in decibels (dB). Fiber optic cable specifications express cable loss as attenuation per 1-km length as dB/km. This value is multiplied by the total length of the optical fiber in kilometers to determine the fiber’s total loss in dB.
Optical fiber light loss is caused by a number of factors that can be categorized into extrinsic and intrinsic losses:
- Extrinsic
- Bending loss
- Splice and connector loss
- Intrinsic
- Loss inherent to fiber
- Loss resulting from fiber fabrication
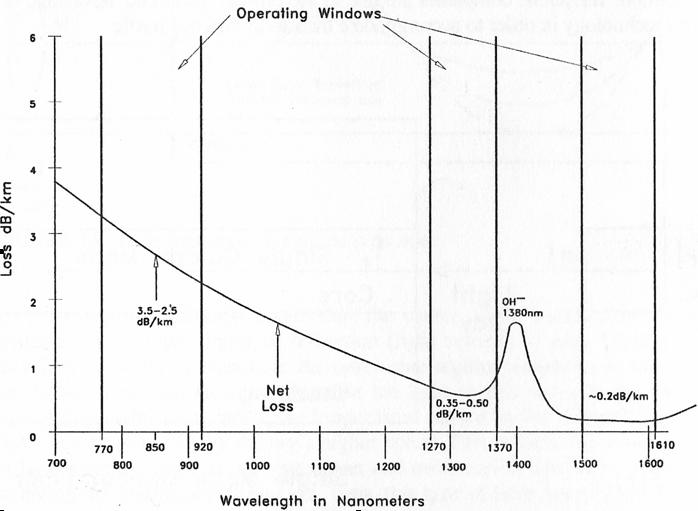
Figure 1. Optical fiber operating wavelengths.
- Fresnel reflection
Bend Loss. Bend loss occurs at fiber cable bends that are tighter than the cable’s minimum bend radius. Bending loss can also occur on a smaller scale from such factors as:
- Sharp curves of thefiber core
- Displacements of a few millimeters or less, caused by buffer or jacket imperfections
- Poor installation practice
This light power loss, called microbending, can add up to a significant amount over a long distance.
Splice and Connector Loss. Splice loss occurs at all splice locations. Mechanical splices usually have the highest loss, commonly ranging from 0.2 to over 1.0 dB, depending on the type of splice. Fusion splices have lower losses, usually less than 0.1 dB. A loss of 0.05 dB or less is usually achieved with good equipment and an experienced splicing crew. High loss can be attributed to a number of factors, including:
- Poor cleave
- Misalignment of fiber cores
- An air gap
- Contamination
- Index-of-refraction mismatch
- Core diameter mismatch to name just a few.
Losses at fiber optic connectors commonly range from 0.25 to over 1.5 dB and depend greatly on the type of connector used. Other factors that contribute to the connection loss include:
- Dirt or contaminants on the connector (very common)
- Improper connector installation
- A damaged connector face
- Poor scribe (cleave)
- Mismatched fiber cores
- Misaligned fiber cores
- Index-of-refraction mismatch
Loss Inherent to Fiber. Light loss in a fiber that cannot be eliminated during the fabrication process is due to impurities in the glass and the absorption of light at the molecular level. Loss of light due to variations in optical density, composition, and molecular structure is called Rayleigh scattering. Rays of light encountering these variations and impurities are scattered in many directions and lost.
The absorption of light at the molecular level in a fiber is mainly due to contaminants in glass such as water molecules (OH-). The ingress of OUT molecules into an optical fiber is one of the main factors contributing to the fiber’s increased attenuation in aging. Silica glass’s (Si02) molecular resonance absorption also contributes to some light loss.
Figure 1 shows the net attenuation of a silica glass fiber and the three fiber operating windows at 850, 1310, and 1550 nm. For long-distance transmissions, 1310- or 1550-nm windows are used. The 1550-nm window has slightly less attenuation than 1310 nm. The 850-nm communication is common in shorter-distance, lower-cost installations.
Loss Resulting from Fiber Fabrication. Irregularities during the manufacturing process can result in the loss of light rays. For example, a 0.1 percent change in the core diameter can result in a 10-dB loss per kilometer. Precision tolerance must be maintained throughout the manufacturing of the fiber to minimize losses.
Fresnel Reflection. Fresnel reflection occurs at any medium boundary where the refractive index changes, causing a portion of the incident light ray to be reflected back into the first medium. The fiber end is a good example of this occurrence. Light, traveling from air to the fiber core, is refracted into the core. However, some of the light, about 4 percent, is reflected back into the air. The amount being reflected can be estimated using the following formula:

At a fiber connector, the light reflected back can easily be seen with an optical time domain reflectometer (OTDR) trace. It appears as a large upward spike in the trace. This reflected light can cause problems if a laser is used and should be kept to a minimum.
The reflected light power can be reduced by using better connectors. Connectors with the “PC” (Physical Contact) or “APC” (Angle Physical Contact) designations are designed to minimize this reflection.
How to Reduce Losses in Optical Fiber?
In order to ensure the output power can be within the sensitivity of the receiver and leave enough margin for the performance degradation with the time, it is an essential issue to reduce the losses in optical fiber. Here are some common approaches in fiber link design and installation.
- Make sure to adapt the high-quality cables with same properties as much as possible.
- Choose qualified connectors as much as possible. Make sure that the insertion loss should be lower than 0.3dB and the additional loss should be lower than 0.2dB.
- Try to use the entire disc to configure (single disc more than 500 meters) in order to minimize the number of joints.
- During splicing, strictly follow the processing and environment requirements.
- The connecting joints must have excellent patch and closed coupling so that can prevent the light leakage.
- Make sure of the cleanliness of the connectors.
- Choose the best route and methods to lay the fiber cables during design the construction.

- Select and form a qualified construction team to guarantee the quality of the construction.
- Strengthen the protection work, especially lightning protection, electrical protection, anti-corrosion and anti mechanical damage.
- Use high quality heat-shrinkable tube.
Summary
When it comes to high-quality fiber patch cables that help in reducing losses in optical fiber, Fiber-Mart offers bend insensitive fiber (BIF) patch cables with ultra low insertion loss (IL) and bend radius, ensuring high performance of data transmission.I believe you can find a suitable fiber optic patch cable for your devices in Fiber-Mart.please contact us: product@fiber-mart.com.








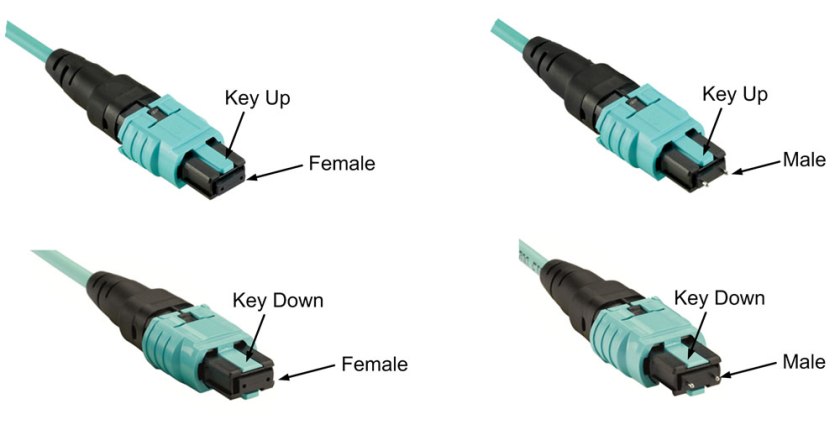

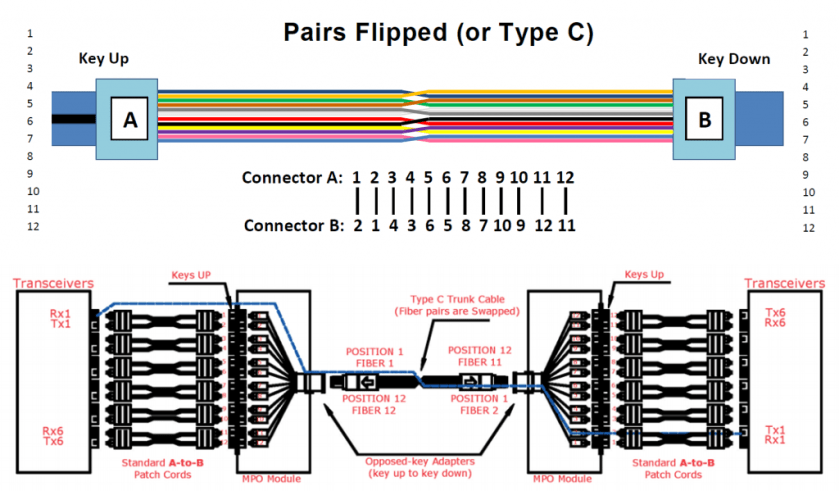
 Since the MTP connectors can either key up and key down, there are two types of MPO adapters.
Since the MTP connectors can either key up and key down, there are two types of MPO adapters.


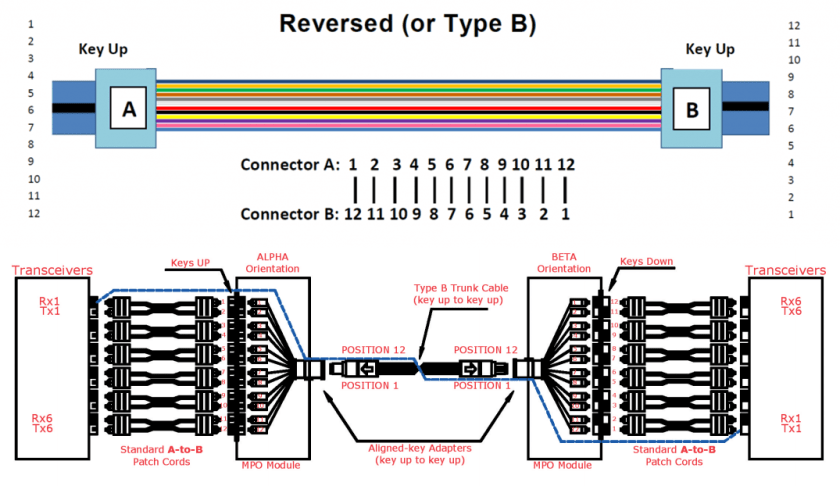 Polarity C
Polarity C